CF1498C.Planar Reflections
普及/提高-
通过率:0%
AC君温馨提醒
该题目为【codeforces】题库的题目,您提交的代码将被提交至codeforces进行远程评测,并由ACGO抓取测评结果后进行展示。由于远程测评的测评机由其他平台提供,我们无法保证该服务的稳定性,若提交后无反应,请等待一段时间后再进行重试。
题目描述
Gaurang has grown up in a mystical universe. He is faced by n consecutive 2D planes. He shoots a particle of decay age k at the planes.
A particle can pass through a plane directly, however, every plane produces an identical copy of the particle going in the opposite direction with a decay age k−1 . If a particle has decay age equal to 1 , it will NOT produce a copy.
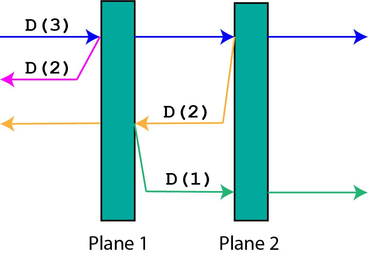
For example, if there are two planes and a particle is shot with decay age 3 (towards the right), the process is as follows: (here, D(x) refers to a single particle with decay age x )
- the first plane produces a D(2) to the left and lets D(3) continue on to the right;
- the second plane produces a D(2) to the left and lets D(3) continue on to the right;
- the first plane lets D(2) continue on to the left and produces a D(1) to the right;
- the second plane lets D(1) continue on to the right ( D(1) cannot produce any copies).
In total, the final multiset S of particles is {D(3),D(2),D(2),D(1)} . (See notes for visual explanation of this test case.)
Gaurang is unable to cope up with the complexity of this situation when the number of planes is too large. Help Gaurang find the size of the multiset S , given n and k .
Since the size of the multiset can be very large, you have to output it modulo 109+7 .
Note: Particles can go back and forth between the planes without colliding with each other.
输入格式
The first line of the input contains the number of test cases t ( 1≤t≤100 ). Then, t lines follow, each containing two integers n and k ( 1≤n,k≤1000 ).
Additionally, the sum of n over all test cases will not exceed 1000 , and the sum of k over all test cases will not exceed 1000 . All test cases in one test are different.
输出格式
Output t integers. The i -th of them should be equal to the answer to the i -th test case.
输入输出样例
输入#1
4 2 3 2 2 3 1 1 3
输出#1
4 3 1 2
输入#2
3 1 1 1 500 500 250
输出#2
1 2 257950823
说明/提示
Let us explain the first example with four test cases.
Test case 1: ( n=2 , k=3 ) is already explained in the problem statement.
See the below figure of this simulation. Each straight line with a different color represents the path of a different particle. As you can see, there are four distinct particles in the multiset. Note that the vertical spacing between reflected particles is for visual clarity only (as mentioned before, no two distinct particles collide with each other)
 Test case 2: ( n=2 , k=2 ) is explained as follows:
Test case 2: ( n=2 , k=2 ) is explained as follows:
- the first plane produces a D(1) to the left and lets D(2) continue on to the right;
- the second plane produces a D(1) to the left and lets D(2) continue on to the right;
- the first plane lets D(1) continue on to the left ( D(1) cannot produce any copies).
Total size of multiset obtained {D(1),D(1),D(2)} is equal to three.
Test case 3: ( n=3 , k=1 ), there are three planes, but decay age is only one. So no new copies are produced while the one particle passes through the planes. Hence, the answer is one.
Test case 4: ( n=1 , k=3 ) there is only one plane. The particle produces a new copy to the left. The multiset {D(2),D(3)} is of size two.