CF1174F.Ehab and the Big Finale
普及/提高-
通过率:0%
AC君温馨提醒
该题目为【codeforces】题库的题目,您提交的代码将被提交至codeforces进行远程评测,并由ACGO抓取测评结果后进行展示。由于远程测评的测评机由其他平台提供,我们无法保证该服务的稳定性,若提交后无反应,请等待一段时间后再进行重试。
题目描述
This is an interactive problem.
You're given a tree consisting of n nodes, rooted at node 1 . A tree is a connected graph with no cycles.
We chose a hidden node x . In order to find this node, you can ask queries of two types:
- d u ( 1≤u≤n ). We will answer with the distance between nodes u and x . The distance between two nodes is the number of edges in the shortest path between them.
- s u ( 1≤u≤n ). We will answer with the second node on the path from u to x . However, there's a plot twist. If u is not an ancestor of x , you'll receive "Wrong answer" verdict!
Node a is called an ancestor of node b if a=b and the shortest path from node 1 to node b passes through node a . Note that in this problem a node is not an ancestor of itself.
Can you find x in no more than 36 queries? The hidden node is fixed in each test beforehand and does not depend on your queries.
输入格式
The first line contains the integer n ( 2≤n≤2⋅105 ) — the number of nodes in the tree.
Each of the next n−1 lines contains two space-separated integers u and v ( 1≤u,v≤n ) that mean there's an edge between nodes u and v . It's guaranteed that the given graph is a tree.
输出格式
To print the answer, print "! x" (without quotes).
Interaction
To ask a question, print it in one of the formats above:
- d u ( 1≤u≤n ), or
- s u ( 1≤u≤n ).
After each question, you should read the answer: either the distance or the second vertex on the path, as mentioned in the legend.
If we answer with −1 instead of a valid answer, that means you exceeded the number of queries, made an invalid query, or violated the condition in the second type of queries. Exit immediately after receiving −1 and you will see Wrong answer verdict. Otherwise, you can get an arbitrary verdict because your solution will continue to read from a closed stream.
After printing a query, do not forget to output end of line and flush the output. Otherwise, you will get Idleness limit exceeded. To do this, use:
- fflush(stdout) or cout.flush() in C++;
- System.out.flush() in Java;
- flush(output) in Pascal;
- stdout.flush() in Python;
- See the documentation for other languages.
Hacks:
The first line should contain two integers n and x ( 2≤n≤2⋅105 , 1≤x≤n ).
Each of the next n−1 lines should contain two integers u and v ( 1≤u,v≤n ) that mean there is an edge between nodes u and v . The edges must form a tree.
输入输出样例
输入#1
5 1 2 1 3 3 4 3 5 3 5
输出#1
d 2 s 3 ! 5
说明/提示
In the first example, the hidden node is node 5 .
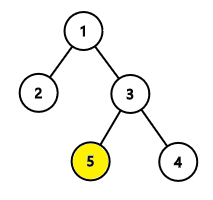 We first ask about the distance between node x and node 2 . The answer is 3 , so node x is either 4 or 5 . We then ask about the second node in the path from node 3 to node x . Note here that node 3 is an ancestor of node 5 . We receive node 5 as the answer. Finally, we report that the hidden node is node 5 .
We first ask about the distance between node x and node 2 . The answer is 3 , so node x is either 4 or 5 . We then ask about the second node in the path from node 3 to node x . Note here that node 3 is an ancestor of node 5 . We receive node 5 as the answer. Finally, we report that the hidden node is node 5 .