CF1153D.Serval and Rooted Tree
普及/提高-
通过率:0%
AC君温馨提醒
该题目为【codeforces】题库的题目,您提交的代码将被提交至codeforces进行远程评测,并由ACGO抓取测评结果后进行展示。由于远程测评的测评机由其他平台提供,我们无法保证该服务的稳定性,若提交后无反应,请等待一段时间后再进行重试。
题目描述
Now Serval is a junior high school student in Japari Middle School, and he is still thrilled on math as before.
As a talented boy in mathematics, he likes to play with numbers. This time, he wants to play with numbers on a rooted tree.
A tree is a connected graph without cycles. A rooted tree has a special vertex called the root. A parent of a node v is the last different from v vertex on the path from the root to the vertex v . Children of vertex v are all nodes for which v is the parent. A vertex is a leaf if it has no children.
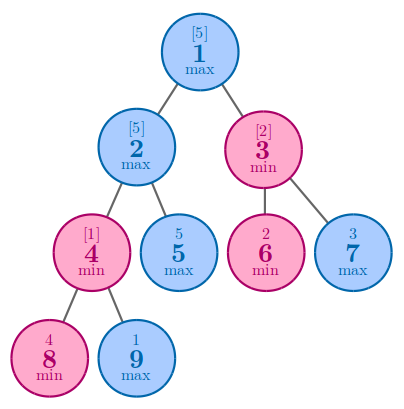
The rooted tree Serval owns has n nodes, node 1 is the root. Serval will write some numbers into all nodes of the tree. However, there are some restrictions. Each of the nodes except leaves has an operation max or min written in it, indicating that the number in this node should be equal to the maximum or minimum of all the numbers in its sons, respectively.
Assume that there are k leaves in the tree. Serval wants to put integers 1,2,…,k to the k leaves (each number should be used exactly once). He loves large numbers, so he wants to maximize the number in the root. As his best friend, can you help him?
输入格式
The first line contains an integer n ( 2≤n≤3⋅105 ), the size of the tree.
The second line contains n integers, the i -th of them represents the operation in the node i . 0 represents min and 1 represents max . If the node is a leaf, there is still a number of 0 or 1 , but you can ignore it.
The third line contains n−1 integers f2,f3,…,fn ( 1≤fi≤i−1 ), where fi represents the parent of the node i .
输出格式
Output one integer — the maximum possible number in the root of the tree.
输入输出样例
输入#1
6 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 2 2 2 2
输出#1
1
输入#2
5 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1
输出#2
4
输入#3
8 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 3
输出#3
4
输入#4
9 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4
输出#4
5
说明/提示
Pictures below explain the examples. The numbers written in the middle of the nodes are their indices, and the numbers written on the top are the numbers written in the nodes.
In the first example, no matter how you arrange the numbers, the answer is 1 .
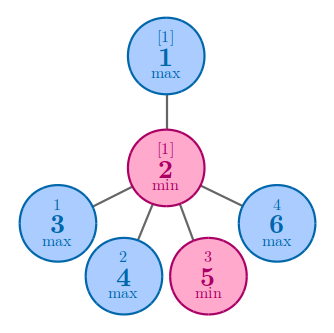 In the second example, no matter how you arrange the numbers, the answer is 4 .
In the second example, no matter how you arrange the numbers, the answer is 4 .
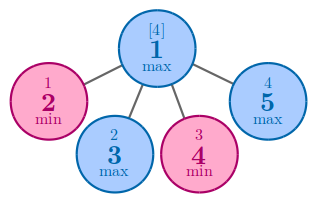 In the third example, one of the best solution to achieve 4 is to arrange 4 and 5 to nodes 4 and 5 .
In the third example, one of the best solution to achieve 4 is to arrange 4 and 5 to nodes 4 and 5 .
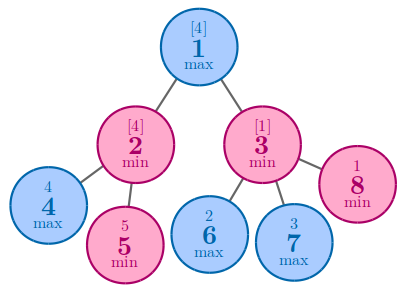 In the fourth example, the best solution is to arrange 5 to node 5 .
In the fourth example, the best solution is to arrange 5 to node 5 .