CF750F.New Year and Finding Roots
普及/提高-
通过率:0%
AC君温馨提醒
该题目为【codeforces】题库的题目,您提交的代码将被提交至codeforces进行远程评测,并由ACGO抓取测评结果后进行展示。由于远程测评的测评机由其他平台提供,我们无法保证该服务的稳定性,若提交后无反应,请等待一段时间后再进行重试。
题目描述
This is an interactive problem. In the interaction section below you will find the information about flushing the output.
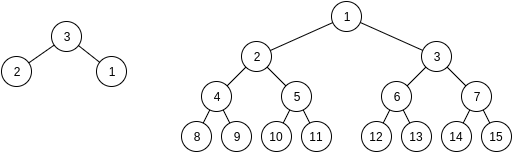
The New Year tree of height h is a perfect binary tree with vertices numbered 1 through 2h−1 in some order. In this problem we assume that h is at least 2 . The drawing below shows one example New Year tree of height 3 :
 Polar bears love decorating the New Year tree and Limak is no exception. To decorate the tree, he must first find its root, i.e. a vertex with exactly two neighbours (assuming that h>=2 ). It won't be easy because Limak is a little bear and he doesn't even see the whole tree. Can you help him?
Polar bears love decorating the New Year tree and Limak is no exception. To decorate the tree, he must first find its root, i.e. a vertex with exactly two neighbours (assuming that h>=2 ). It won't be easy because Limak is a little bear and he doesn't even see the whole tree. Can you help him?
There are t testcases. In each testcase, you should first read h from the input. Then you can ask at most 16 questions of format "? x" (without quotes), where x is an integer between 1 and 2h−1 , inclusive. As a reply you will get the list of neighbours of vertex x (more details in the "Interaction" section below). For example, for a tree on the drawing above after asking "? 1" you would get a response with 3 neighbours: 4 , 5 and 7 . Your goal is to find the index of the root y and print it in the format "! y". You will be able to read h for a next testcase only after printing the answer in a previous testcase and flushing the output.
Each tree is fixed from the beginning and it doesn't change during your questions.
输入格式
The first line of the input contains a single integer t ( 1<=t<=500 ) — the number of testcases.
At the beginning of each testcase you should read from the input a single integer h ( 2<=h<=7 ) — the height of the tree. You can't read the value of h in a next testcase until you answer a previous testcase.
输出格式
To ask a question about neighbours of vertex x , print "? x" (without quotes) on a separate line. Note, you must print an end-of-line character after the last character of the line and flush your output to get a response.
The response will consist of two lines. The first line will contain a single integer k ( 1<=k<=3 ) — the number of neighbours of vertex x . The second line will contain k distinct integers t1,...,tk ( 1<=t_{1}<...<t_{k}<=2^{h}-1 ) — indices of neighbours of vertex x , gives in the increasing order.
After asking at most 16 questions you have to say y — the index of the root. Print "! y" (without quotes) and an end-of-line character, and flush the output.
Each tree is fixed from the beginning and it doesn't change during your questions.
You can get Idleness Limit Exceeded if you don't print anything or if you forget to flush the output.
To flush you can use (just printing a query/answer and end-of-line):
- fflush(stdout) in C++;
- System.out.flush() in Java;
- stdout.flush() in Python;
- flush(output) in Pascal;
- See the documentation for other languages.
In any moment if the program reads h=0 or k=0 it should immediately terminate normally (for example, calling exit(0)). It means that the system detected incorrect request/output from your program and printed 0 because if can't process your requests anymore. In this case you'll receive verdict "Wrong Answer", but if you ignore case h=0 or k=0 it could lead to "Runtime Error", "Time/Memory limit exceeded" or any other verdict because your program could read a trash from the closed input stream.
Hacking. To hack someone, use the following format:
The first line should contain a single integer t equal to 1 (only one testcase is allowed in hacks). The second line should contain a single integer h . Each of next 2h−2 lines should contain two distinct integers ai and bi ( 1<=ai,bi<=2h−1 ), denoting two nodes connected with an edge. The printed edges must form a perfect binary tree of height h .
Of course, contestant programs will not be able to see this input.
输入输出样例
输入#1
1 3 3 4 5 7 2 1 2 1 2
输出#1
? 1 ? 5 ? 6 ! 5
输入#2
2 2 1 3 2 1 2 2 1 2 4 3 3 12 13
输出#2
? 1 ? 3 ? 3 ! 3 ? 6 ! 1
说明/提示
In the first sample, a tree corresponds to the drawing from the statement.
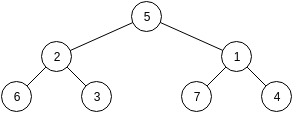
In the second sample, there are two two testcases. A tree in the first testcase has height 2 and thus 3 vertices. A tree in the second testcase has height 4 and thus 15 vertices. You can see both trees on the drawing below.