CF618D.Hamiltonian Spanning Tree
普及/提高-
通过率:0%
AC君温馨提醒
该题目为【codeforces】题库的题目,您提交的代码将被提交至codeforces进行远程评测,并由ACGO抓取测评结果后进行展示。由于远程测评的测评机由其他平台提供,我们无法保证该服务的稳定性,若提交后无反应,请等待一段时间后再进行重试。
题目描述
A group of n cities is connected by a network of roads. There is an undirected road between every pair of cities, so there are 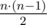 roads in total. It takes exactly y seconds to traverse any single road.
roads in total. It takes exactly y seconds to traverse any single road.
A spanning tree is a set of roads containing exactly n−1 roads such that it's possible to travel between any two cities using only these roads.
Some spanning tree of the initial network was chosen. For every road in this tree the time one needs to traverse this road was changed from y to x seconds. Note that it's not guaranteed that x is smaller than y .
You would like to travel through all the cities using the shortest path possible. Given n , x , y and a description of the spanning tree that was chosen, find the cost of the shortest path that starts in any city, ends in any city and visits all cities exactly once.
输入格式
The first line of the input contains three integers n , x and y ( 2<=n<=200000,1<=x,y<=109 ).
Each of the next n−1 lines contains a description of a road in the spanning tree. The i -th of these lines contains two integers ui and vi ( 1<=ui,vi<=n ) — indices of the cities connected by the i -th road. It is guaranteed that these roads form a spanning tree.
输出格式
Print a single integer — the minimum number of seconds one needs to spend in order to visit all the cities exactly once.
输入输出样例
输入#1
5 2 3 1 2 1 3 3 4 5 3
输出#1
9
输入#2
5 3 2 1 2 1 3 3 4 5 3
输出#2
8
说明/提示
In the first sample, roads of the spanning tree have cost 2 , while other roads have cost 3 . One example of an optimal path is 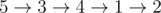 .
.
In the second sample, we have the same spanning tree, but roads in the spanning tree cost 3, while other roads cost 2. One example of an optimal path is 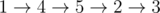 .
.